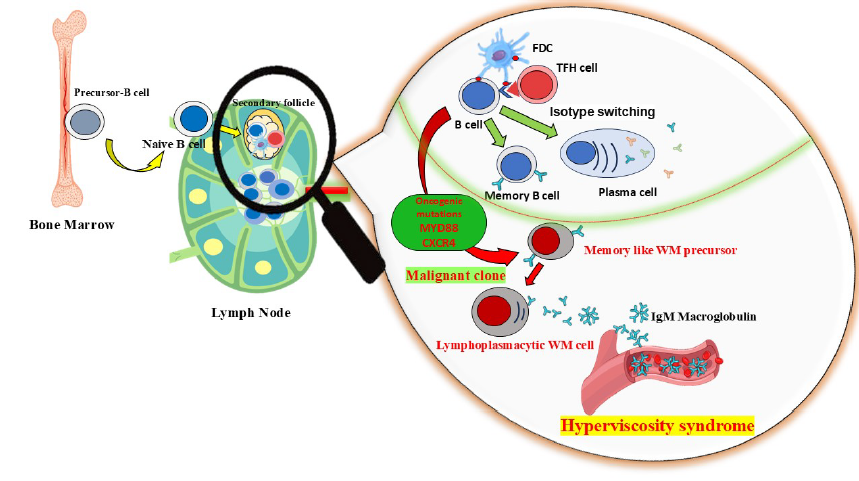
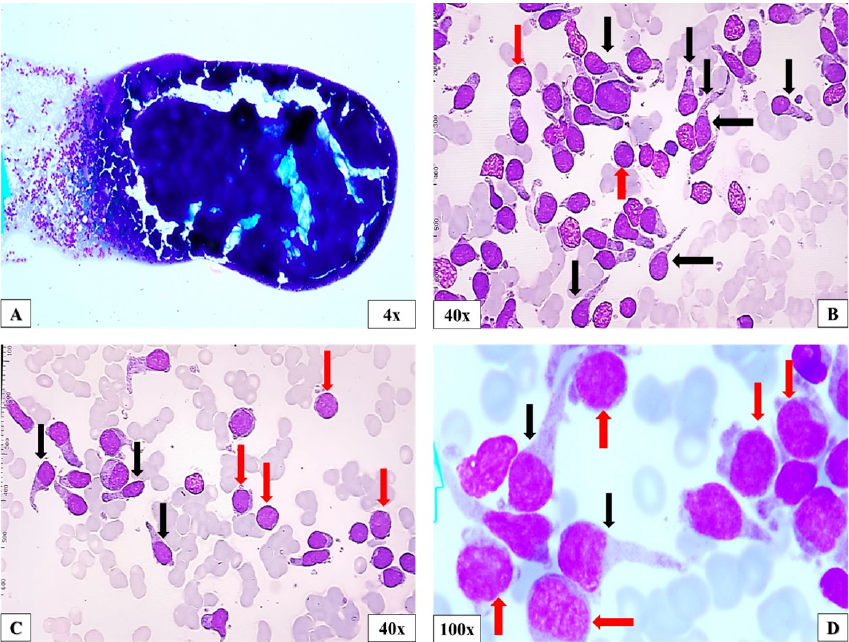
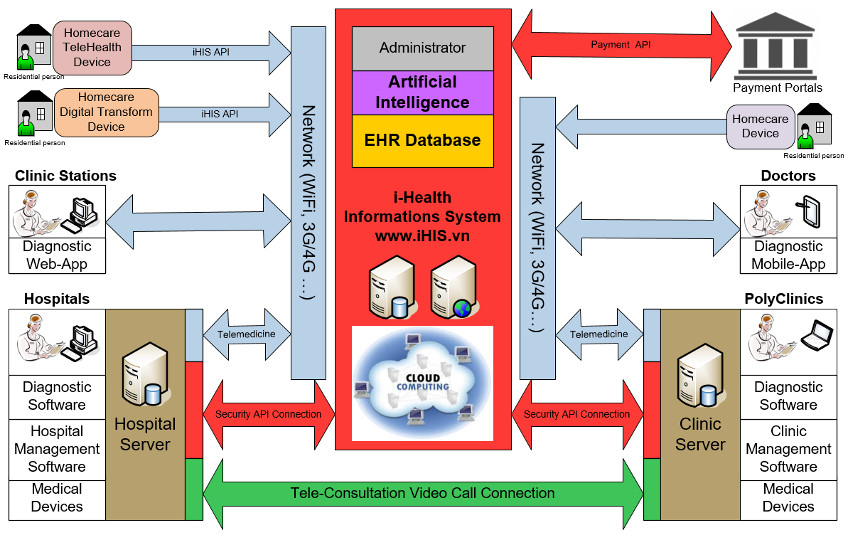
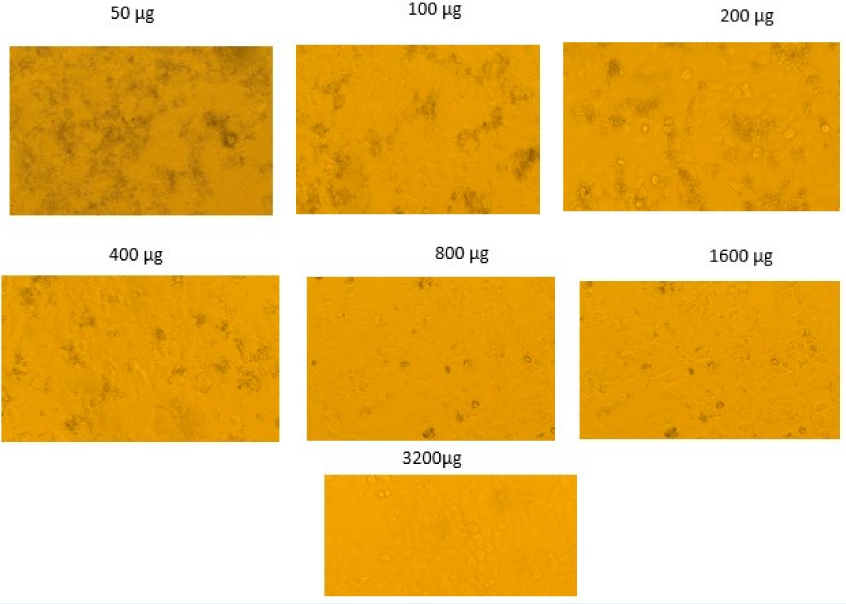
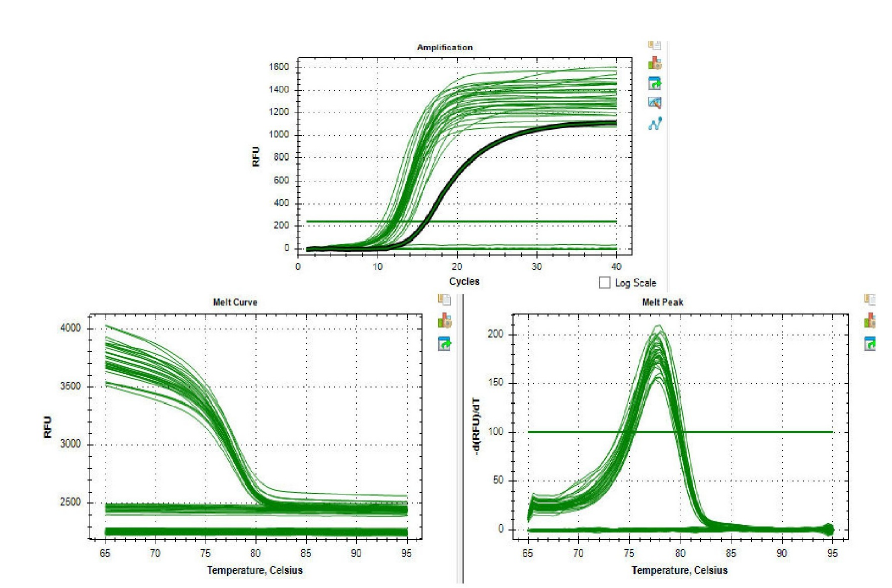
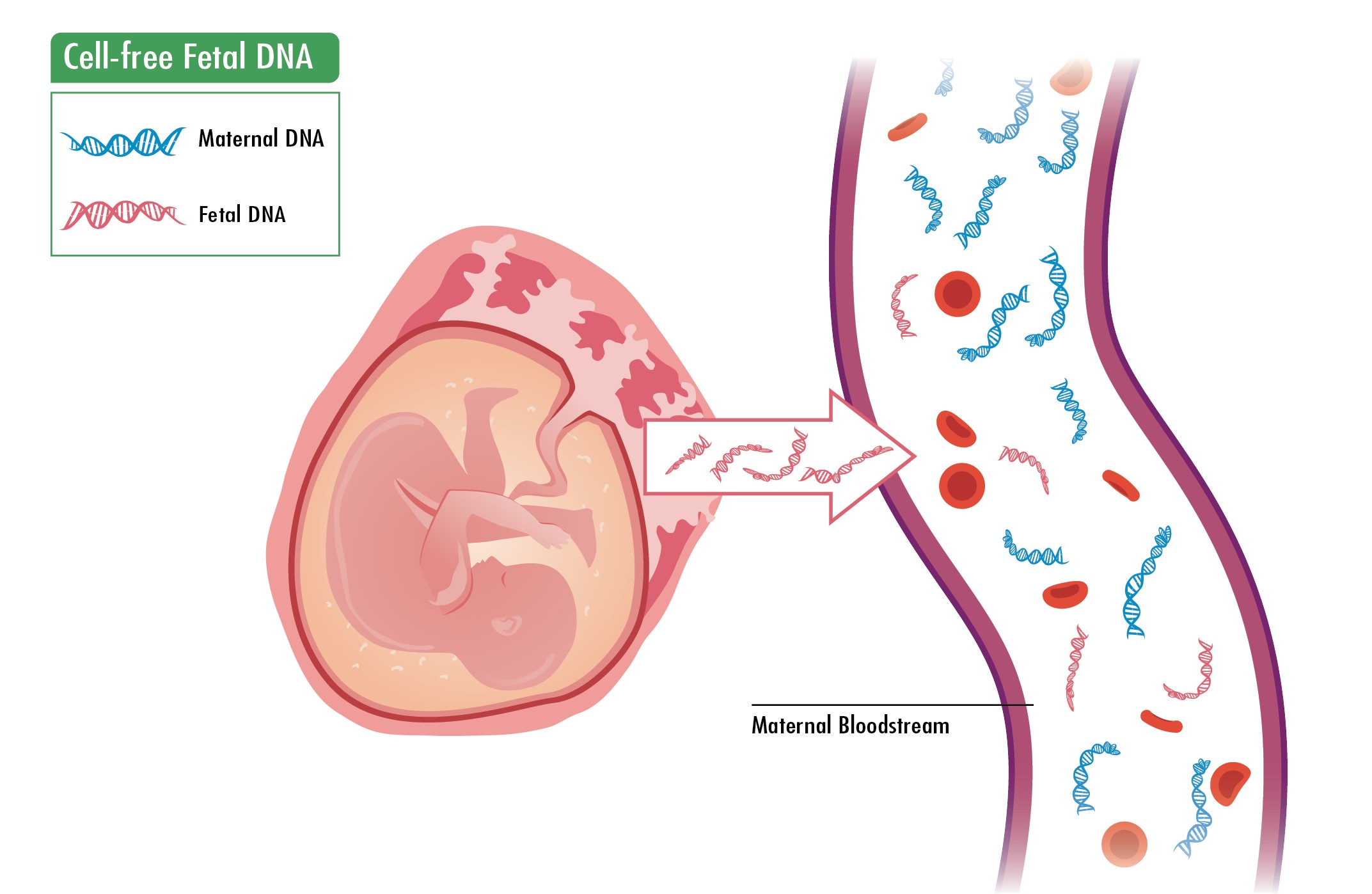
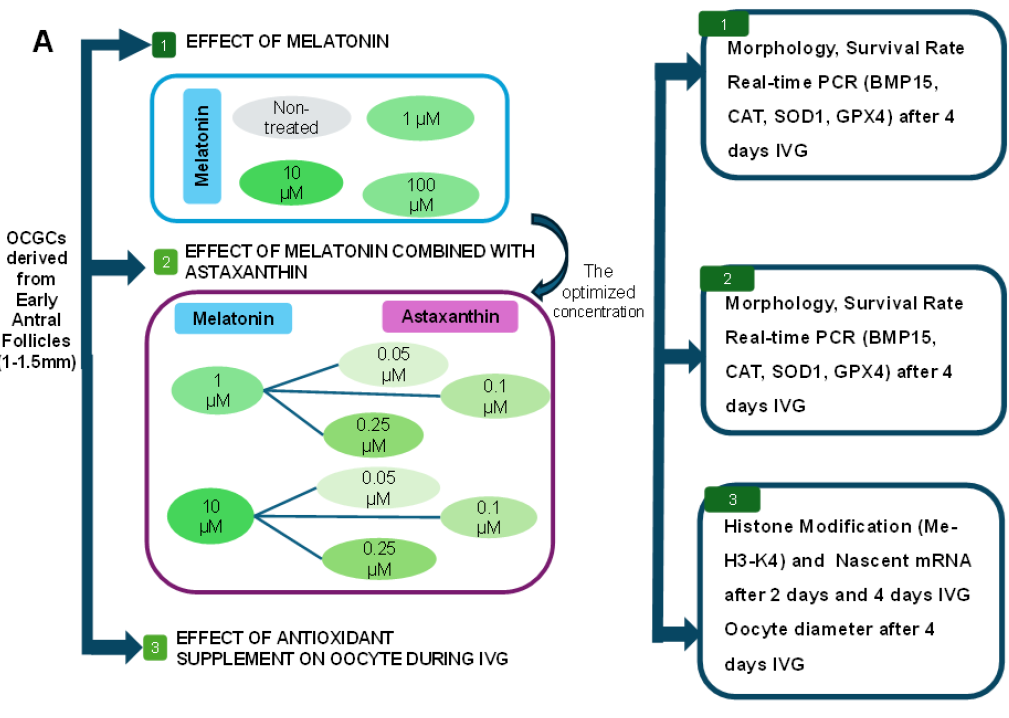
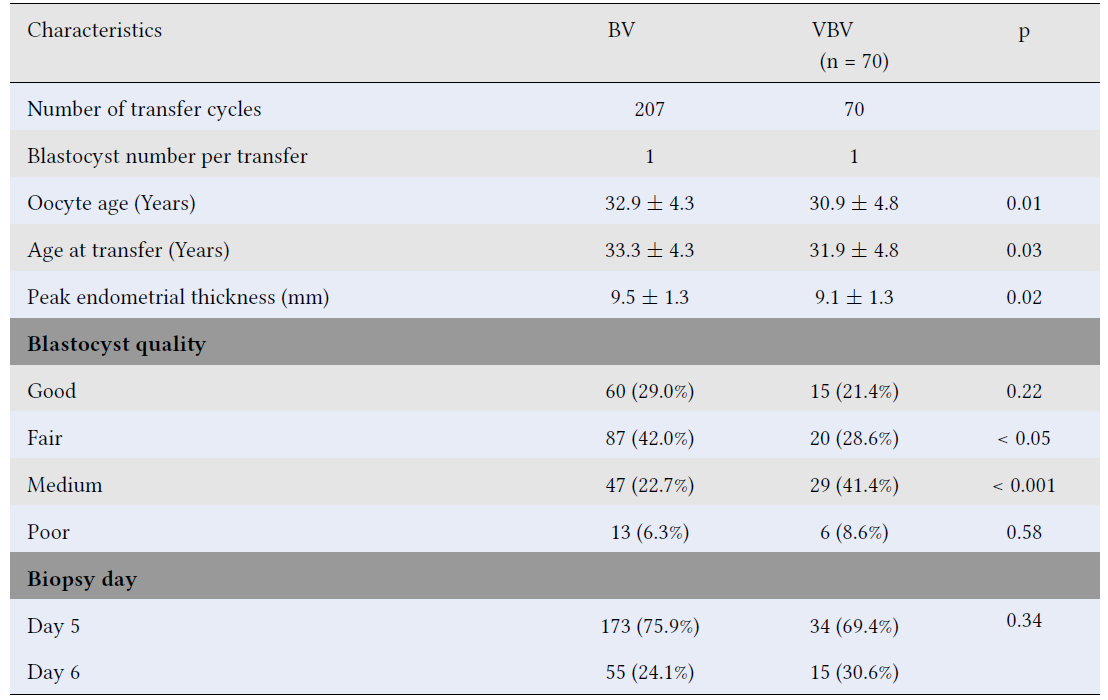
Biomedical Research and Therapy (Online ISSN 2198-4093) publishes 12 peer-reviewed issues each year, covering a wide range of biomedical and clinical sciences. Unlike many open-access journals, which charge authors for publication while providing free reader access, Biomedical Research and Therapy does not require fees for subscription, submission, processing, publication, or color image reproduction. Recognized internationally, this journal is committed to disseminating high-quality research in an open-access format, emphasizing basic, translational, and clinical studies on molecular therapeutics and cellular therapies. It includes research involving animal models and clinical trials. The rigorous peer-review process ensures that only scientifically, technically, and ethically sound articles adhering to standard reporting guidelines are published. The journal’s editorial policies are in strict alignment with standards set by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE), the World Association of Medical Editors (WAME), and the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE), upholding the highest principles of publication ethics.
Biomedical Research and Therapy (Online ISSN 2198-4093) is the official journal of the VNUHCM-US Stem Cell Institute, Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam. This journal is managed and published by Biomedpress on behalf of the owners, the VNUHCM-US Stem Cell Institute, Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam.